
Mental and Emotional Health
"Let's Learn, Explore, and Connect to the World"

The Role of Nutrition in Mental Health: What the Science Says
- Patricia Santos
- Mental and Emotional Health
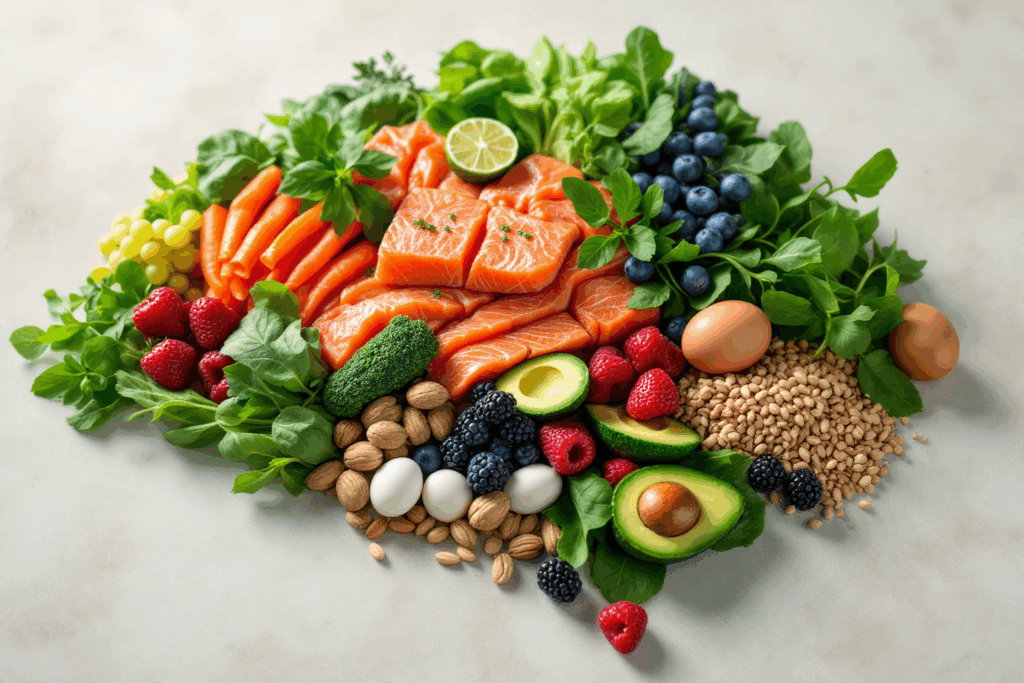
Introduction
 Lately, the link between nutrition and mental health has garnered significant interest from researchers, medical professionals, and the general public. This burgeoning field of study explores how what we eat directly affects the way we feel, think, and behave. Traditional diets, once evaluated solely for their physical health benefits, are now being scrutinized for their impact on mental well-being. As the global burden of mental health disorders continues to rise, understanding the potential of dietary strategies to alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mental conditions is more crucial than ever.
Lately, the link between nutrition and mental health has garnered significant interest from researchers, medical professionals, and the general public. This burgeoning field of study explores how what we eat directly affects the way we feel, think, and behave. Traditional diets, once evaluated solely for their physical health benefits, are now being scrutinized for their impact on mental well-being. As the global burden of mental health disorders continues to rise, understanding the potential of dietary strategies to alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mental conditions is more crucial than ever.
 This exploration is not merely academic; it has profound practical implications for daily living. The adage “you are what you eat” extends beyond physical health, suggesting that our food choices might influence our emotional and cognitive functions. This blog aims to unpack what current science says about the role of nutrition in mental health. By delving into how different nutrients, diets, and eating patterns affect mental health, we seek to provide insights that can help individuals make informed dietary choices for both physical and mental well-being. Join us in examining the intricate connection between our diet and mental health, supported by the newest scientific findings.
This exploration is not merely academic; it has profound practical implications for daily living. The adage “you are what you eat” extends beyond physical health, suggesting that our food choices might influence our emotional and cognitive functions. This blog aims to unpack what current science says about the role of nutrition in mental health. By delving into how different nutrients, diets, and eating patterns affect mental health, we seek to provide insights that can help individuals make informed dietary choices for both physical and mental well-being. Join us in examining the intricate connection between our diet and mental health, supported by the newest scientific findings.
Understanding Mental Health
 Mental health encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how we think, feel, and behave in daily life. It influences our stress management, our relationships with others, and our decision-making processes. Mental health is essential to our ability, both collectively and individually, to process thoughts, experience emotions, engage socially, work, and appreciate life. Consequently, the advancement, safeguarding, and recovery of mental health are critical concerns for individuals, communities, and societies worldwide.
Mental health encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how we think, feel, and behave in daily life. It influences our stress management, our relationships with others, and our decision-making processes. Mental health is essential to our ability, both collectively and individually, to process thoughts, experience emotions, engage socially, work, and appreciate life. Consequently, the advancement, safeguarding, and recovery of mental health are critical concerns for individuals, communities, and societies worldwide.
 With conditions such as depression and anxiety on the rise globally, understanding the underlying factors that contribute to mental health is more important than ever. Depression is a primary cause of disability around the world, impacting nearly 264 million people globally. Additionally, millions suffer from anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and various phobias. These disorders can significantly impair an individual’s ability to function daily and can lead to profound personal and social consequences.
With conditions such as depression and anxiety on the rise globally, understanding the underlying factors that contribute to mental health is more important than ever. Depression is a primary cause of disability around the world, impacting nearly 264 million people globally. Additionally, millions suffer from anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and various phobias. These disorders can significantly impair an individual’s ability to function daily and can lead to profound personal and social consequences.
Despite the increasing visibility of mental health issues, there remains a pervasive stigma associated with admitting to mental health struggles, which can hinder individuals from seeking help. Mental health isn’t just about avoiding problems – it’s about thriving! It means having the ability to live a rich and fulfilling life where you can tap into your creativity and embrace new experiences. It also includes the strength and resilience to bounce back from challenges that life throws your way. So, mental health is about feeling good and functioning well, not just the absence of illness. Effective strategies for maintaining mental health and wellness are thus crucial not only for preventing or managing mental illness but also for ensuring quality of life and overall health.
 In this context, the role of nutrition—often underappreciated—can be significant. It turns out what you eat isn’t just about your physical health – it can also affect your mental well-being! Recent studies show a strong connection between diet and mental health. The food you choose can influence everything from how your brain functions to how stable your emotions feel. So, just like taking care of your body through diet, making healthy food choices can be a big step towards taking care of your mind, too. By understanding the essential role that proper nutrition plays in mental health, we can better equip ourselves to maintain it in a holistic and effective manner.
In this context, the role of nutrition—often underappreciated—can be significant. It turns out what you eat isn’t just about your physical health – it can also affect your mental well-being! Recent studies show a strong connection between diet and mental health. The food you choose can influence everything from how your brain functions to how stable your emotions feel. So, just like taking care of your body through diet, making healthy food choices can be a big step towards taking care of your mind, too. By understanding the essential role that proper nutrition plays in mental health, we can better equip ourselves to maintain it in a holistic and effective manner.
Fundamentals of Nutrition
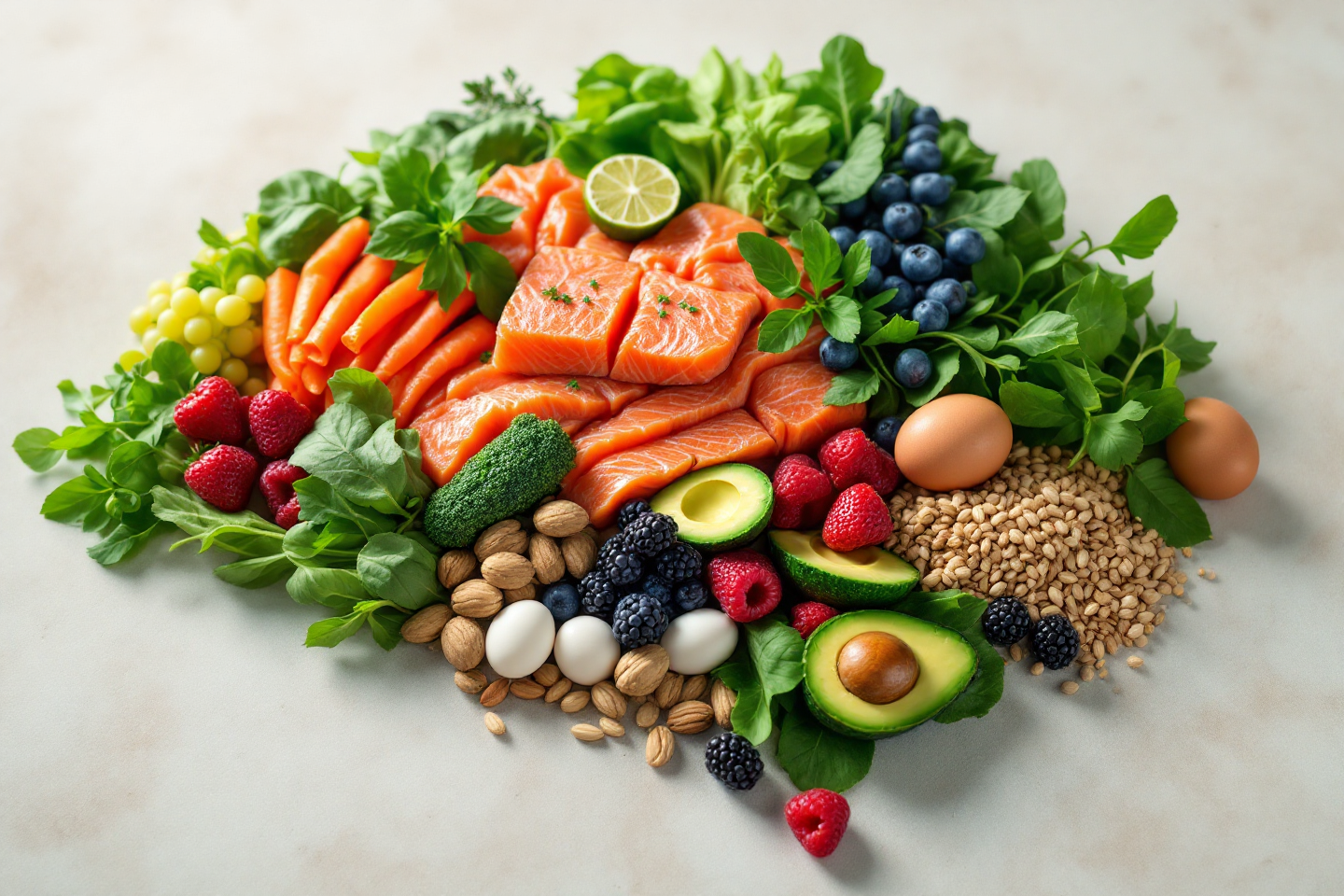
Nutrition is vital for overall health, including mental wellness. It supplies the essential components needed for the body to create enzymes, hormones, and neurotransmitters that regulate brain activity. A balanced diet helps sustain the brain’s structure and protects it against oxidative stress, which can damage brain cells.

Macronutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are crucial for maintaining brain health. Carbohydrates are the brain’s primary source of energy. They influence mood and brain function by providing glucose and impacting the synthesis and release of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. Proteins, broken down into amino acids, are critical for neurotransmitter function, which directly affects mood and cognition. Fats, mainly omega-3 fatty acids, are essential for the structural integrity of the brain. They form cell membranes and are crucial for the development and function of the brain and nervous system.
 Micronutrients are equally vital. Minerals and vitamins such as vitamin D, B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and zinc play significant roles in brain function. For example, B vitamins are involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and energy production. Vitamin D is associated with regulating mood and cognitive abilities. Zinc and magnesium are crucial for neurotransmitter activity, and a deficiency in these can lead to depressive symptoms.
Micronutrients are equally vital. Minerals and vitamins such as vitamin D, B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and zinc play significant roles in brain function. For example, B vitamins are involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and energy production. Vitamin D is associated with regulating mood and cognitive abilities. Zinc and magnesium are crucial for neurotransmitter activity, and a deficiency in these can lead to depressive symptoms.
 Antioxidants, found in various fruits and vegetables, combat oxidative stress that may lead to neuronal damage. Foods rich in antioxidants can thus support brain health by protecting against cell damage.
Antioxidants, found in various fruits and vegetables, combat oxidative stress that may lead to neuronal damage. Foods rich in antioxidants can thus support brain health by protecting against cell damage.
Understanding the impact of these nutrients on the brain illustrates why a nutritious diet is important for mental health. Deficiencies in specific nutrients can lead to changes in brain function, manifesting as mood disorders or cognitive decline. For both your mind and body to thrive, you need a rainbow on your plate! Fuel your brain for peak performance! Imagine your brain as a high-performance computer. Ditch the junk food and feed your brain a feast! A balanced diet with minerals, vitamins, and healthy fats is like a gourmet meal for your mind. It provides all the essential building blocks your brain craves to keep you feeling focused, energized, and ready to conquer your day. So next time you’re making food choices, think about giving your brain the upgrade it deserves! It’s like giving your brain all the tools it needs to stay sharp and resilient.
Scientific Insights into Nutrition and Mental Health
The expanding discipline of nutritional psychiatry investigates the connection between diet and mental health, offering strong evidence that our dietary choices greatly affect our brain function and emotional health. A variety of studies have illuminated this connection, underscoring the potential of dietary interventions in preventing and managing mental health disorders.
Research Findings

Numerous extensive epidemiological studies have established a solid link between a nutritious diet and a lower risk of depression and anxiety. Studies are showing a real connection between food and mood. For example, a research project called the SMILES trial was one of the first to look at how changing your diet can affect mental health. In this study, people who followed a Mediterranean diet for three months felt a significant improvement in their depression symptoms compared to a group that just received support and didn’t change their diet. This suggests that what you eat can be a powerful tool for managing your mental well-being. This study highlighted not just the potential for dietary changes to effect significant improvement in depressive symptoms but also its cost-effectiveness and accessibility as a treatment strategy.
Likewise, studies on the ketogenic diet, which is rich in fats and low in carbohydrates, indicate that it might help reduce symptoms of depression and bipolar disorder. The diet’s impact on brain chemistry, particularly its ability to stabilize neurotransmitter levels and reduce inflammation, is thought to account for these benefits.
Nutrient Deficiencies and Mental Health

Not getting enough of certain nutrients can really impact your mood. Studies have shown that low levels of things like omega-3s, zinc, magnesium, and B vitamins can be linked to a higher risk of feeling down or anxious. Omega-3s are especially important for brain health because they influence chemicals in your brain called neurotransmitters, which play a role in mood. Vitamin D is also crucial for your brain’s development and how it works, and if you don’t have enough, you might be more prone to mood disorders. So, making sure you get the right nutrients is important for both your physical and mental health!
The Inflammatory Hypothesis of Depression

There is increasing evidence supporting the inflammatory hypothesis of depression, which posits that inflammation significantly contributes to the condition. Research suggests a strong link between diet and mood. Diets loaded with sugary treats and fatty foods can crank up inflammation in your body, which might be linked to feeling down. On the other hand, filling your plate with colorful fruits and veggies, fish, and whole grains is packed with anti-inflammatory goodness. This can help keep inflammation in check and potentially improve your mood. So, next time you’re making choices at the grocery store, keep in mind that healthy foods can be a mood booster, too!
Implications for Mental Health Treatment

Eating healthy isn’t a magic bullet for mental health, but science shows it can be a game-changer. Imagine your mental well-being as a puzzle. A balanced diet can be a key piece that fits alongside other treatments to create a strong overall plan. By taking care of your nutrition, you’re taking an important step toward feeling your best. Nutritional interventions can be used alongside medication and psychotherapy to enhance outcomes. For healthcare professionals, understanding the nutritional basis of mental health can be crucial in advising and treating patients with dietary modifications that may improve clinical outcomes.
These insights into the relationship between diet and mental health not only reinforce the importance of a balanced diet for maintaining overall health but also highlight the potential for targeted nutritional interventions in mental health care. As research continues to evolve, it is likely that dietary recommendations will become increasingly tailored to individual mental health conditions, enhancing the efficacy of traditional treatment methods.
Impact of Specific Diets on Mental Health
The influence of specific dietary patterns on mental health has garnered significant interest in recent years. Research has particularly focused on how certain diets — like Mediterranean, ketogenic, and plant-based diets — impact mental well-being, often contrasting these with the effects of diets high in processed foods and sugars.
Mediterranean Diet

The Mediterranean diet might be more than just delicious food for sunny vacations! Packed with vegetables, fruits, nuts, whole grains, and fish, it’s known for its focus on healthy fats like olive oil. Research suggests this way of eating can benefit your mental health, too. The Mediterranean diet is loaded with brain-boosting nutrients like omega-3s, antioxidants, and fiber. These work together to fight inflammation, which can be linked to depression. Studies like the Predimed trial even show that people who stick to this diet tend to have a lower risk of feeling down over time. So, the next time you’re looking for ways to support your mental well-being, consider filling your plate with some Mediterranean sunshine!
Ketogenic Diet

The ketogenic diet, which is low in carbohydrates and high in fats, forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates. Originally developed as a treatment for epilepsy, recent findings suggest that it may also benefit mental health by stabilizing mood and reducing symptoms in conditions like depression and bipolar disorder. The diet enhances the production of ketones in the body, which provides an alternative energy source for the brain and helps increase levels of neurotransmitters like GABA, which can promote relaxation and reduce anxiety. Sticking with the keto diet for a long time can be tough, and the jury’s still out on exactly how much it helps or hurts your mental health in the long run. More research is needed to get a clearer picture of its pros and cons for your mood and overall well-being.
Plant-Based Diets

Plant-based diets, which are high in vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, are also beneficial for mental health. These diets ditch processed foods and focus on whole foods instead. They’re packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients act like tiny warriors in your body, fighting off free radicals (unstable molecules) that can damage cells and contribute to inflammation. Less inflammation might mean a happier, healthier you! Observational studies have linked vegetarian and vegan diets with lower levels of depression compared to diets high in meat and animal products, suggesting that plant-based nutrients may play a role in improving mood.
High Sugar and Processed Foods Diets

Conversely, diets high in refined sugars and processed foods are detrimental to mental health. Skip the fries and sugary drinks! This type of diet might be bringing you down more than you realize. Research shows a strong link between fast food and sugary treats and feeling low or anxious. These diets can trigger inflammation, mess with your gut health, and cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, all of which can zap your mood and energy. So, the next time you’re reaching for a quick bite, think twice – a healthier choice could be a mood-booster in disguise!
What you eat can have a big impact on how you feel. Filling your plate with whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, veggies, and whole grains gives your body the nutrients it needs to thrive. This can have a positive effect on your mental health, too! On the other hand, diets loaded with sugary treats and processed foods might be dragging you down more than you realize. Studies show a link between these unhealthy choices and feeling low or anxious. So, the next time you’re making food choices, remember that healthy eating can be a delicious way to boost your mood and well-being! Tailoring one’s diet to include more anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods can be a strategic part of managing and potentially improving mental health outcomes.
Role of Gut Health in Mental Well-being
The connection between the gut and the brain, often referred to as the gut-brain axis, is a critical area in understanding mental health. Recent scientific advances have shed light on how gut health significantly influences mental well-being, emphasizing the importance of a healthy microbiome.
The Gut-Brain Axis
It’s a surprising fact, but your gut and brain are actually best buds! They have a direct line of communication, constantly sending messages back and forth. This amazing network is called the gut-brain axis, and it plays a big role in how you feel both physically and mentally. This amazing network called the gut-brain axis, connects your feelings and thinking (like your emotions and memory) in your brain with what’s going on down in your intestines. It’s a complex system, but basically, your gut health can influence your mental well-being and vice versa. This bidirectional pathway is mediated by various mechanisms, including neural, immune, endocrine, and humoral links. For instance, the vagus nerve is one of the primary connections between the brain and the gut, transmitting signals in both directions.
Microbiome and Mental Health
There’s a whole universe of tiny creatures living inside your gut! These bacteria aren’t just hanging out – they play a super important role in digestion, keeping bad guys out, and even producing essential nutrients and brain chemicals. Research suggests that the specific mix of these gut bacteria can influence the production of mood-regulating chemicals like serotonin (mostly made in the gut!) and GABA. So, the health of your gut bacteria might be linked to how you feel! Imbalances in gut bacteria can lead to dysregulation of these pathways, potentially contributing to anxiety and depression.
Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Mental Health
Interventions that target gut health, such as the consumption of probiotics and prebiotics, can influence mental health outcomes. Think of your gut as a garden. Probiotics are like friendly new plants you add to help the good stuff grow. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are like fertilizer that nourishes the existing beneficial bacteria already in your gut, helping them thrive. Both probiotics and prebiotics contribute to a healthy gut environment. Studies have suggested that supplements containing probiotics can improve symptoms of depression and anxiety, likely by strengthening the gut-brain axis.
Diet and Gut Health
There’s a fascinating link between your gut and your mood! It turns out the tiny bacteria living inside you (called gut microbiome) play a big role in how you feel. Those delicious fruits, veggies, and whole grains aren’t just good for you – they’re like a superfood for the good bacteria living in your gut! Just like plants need fertilizer to flourish, these good bacteria benefit from the nutrients in these healthy foods. When they thrive, they contribute to a healthy gut environment, which research suggests can even impact your mood in a positive way. On the other hand, processed foods and sugary drinks can harm them. Since a healthy gut seems to be connected to a happy mind, this is a strong reason to choose gut-friendly foods. It’s like giving your mental health a natural boost from the inside out! Research on the gut-brain connection is ongoing, but so far, it suggests that taking care of your gut microbiome through diet could be a powerful tool for managing mental well-being.
Practical Tips for Improving Mental Health Through Diet
Adopting a diet that benefits mental health doesn’t require drastic changes. Instead, small, sustainable adjustments can make a significant difference. Here are some practical tips for incorporating nutritional strategies into everyday life to enhance mental well-being:
- Prioritize Whole Foods:
 Ditch the processed stuff and fill your plate with a rainbow of goodness! Fill your plate with a rainbow of goodness! Choose fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats to fuel your body and mind. These nutrient powerhouses provide the essential building blocks your brain needs to function at its best. Plus, they support your overall health and well-being, keeping you feeling energized and ready to take on the day.
Ditch the processed stuff and fill your plate with a rainbow of goodness! Fill your plate with a rainbow of goodness! Choose fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats to fuel your body and mind. These nutrient powerhouses provide the essential building blocks your brain needs to function at its best. Plus, they support your overall health and well-being, keeping you feeling energized and ready to take on the day.
- Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids like fish (salmon, mackerel, and sardines), flaxseeds, and walnuts in your diet. Omega-3s are known to reduce inflammation and are linked to improved mood and cognitive function.
- Stay Hydrated:
Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal brain function and overall health. Make sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugars:
Reduce intake of foods high in refined sugars and processed ingredients, which can exacerbate inflammation and impact mood stability.
- Consult with Professionals:
It’s commendable to strive for a healthier diet. f you have any existing health concerns, a chat with your doctor or a dietitian is a must before making big dietary changes. This ensures a personalized approach that effectively meets your unique nutritional needs. They can help you create a personalized plan that ensures you’re getting all the nutrients your body needs to thrive. Think of it as getting expert advice to make sure your healthy eating journey is safe and effective!
These simple steps can help individuals leverage the power of nutrition to support their mental health, contributing to a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.
Conclusion
 It’s exciting to see how much science is revealing about the link between food and mood! We used to think about food just as fuel for our bodies, but research now shows it can also play a major role in our mental well-being. Choosing whole foods, omega-3s, and probiotics while limiting processed foods and sugar can significantly boost how we feel. As we learn more about the gut-brain connection and how it’s influenced by what we eat, it’s becoming clear that our dietary choices are a powerful tool for taking care of our mental health. So next time you reach for a snack, remember – you might be giving your brain a boost along with your body! Empowered with this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions to support both their physical and mental health.
It’s exciting to see how much science is revealing about the link between food and mood! We used to think about food just as fuel for our bodies, but research now shows it can also play a major role in our mental well-being. Choosing whole foods, omega-3s, and probiotics while limiting processed foods and sugar can significantly boost how we feel. As we learn more about the gut-brain connection and how it’s influenced by what we eat, it’s becoming clear that our dietary choices are a powerful tool for taking care of our mental health. So next time you reach for a snack, remember – you might be giving your brain a boost along with your body! Empowered with this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions to support both their physical and mental health.
References
- Diet May Be As Important To Mental Health As It Is To Physical Health. (n.d.). Brain Health Education and Research Institute. http://www.brainhealtheducation.org/diet-may-be-as-important-to-mental-health-as-it-is-to-physical-health/
- Nutritional Psychiatry: Emerging Evidence and Expert Interview. (n.d.). Psychiatry Advisor. https://www.psychiatryadvisor.com/home/topics/mood-disorders/nutritional-psychiatry-emerging-evidence-and-expert-interview/
- Research Connects Nutrition and Mental Health. (n.d.). Beautiful Minds Wellness. https://beautifulmindswellness.org/custom-post/research-connects-nutrition-and-mental-health/
- Molendijk, M., Molero, P., Sanchez-Pedreno, F., Does, W. V. D., & Martinez-Gonzalez, M. (2018). Diet quality and depression risk: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Journal of Affective Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.09.022
- 5 Natural Treatments for Depression: How to do it right? (n.d.). GuideMyMind. https://guidemymind.com/natural-treatments-for-depression/
Latest Blogs

Shoppable Posts & Instagram Shopping: Turning Your Profile Into a Seamless Sales Channel
Digital Marketing Blogs “Let’s Learn, Explore, and Connect to the World” Shoppable Posts & Instagram Shopping: Turning Your Profile Into a Seamless Sales Channel Introduction

Past Perfect Continuous 1
English Blogs “Let’s Learn, Explore, and Connect to the World” Past Perfect Continuous 1 I. Introduction to the Past Perfect Continuous Tense in English The
Reading comprehension quiz
Check out our books and more!

Comic Collections : A Compilation of Daily Professional and Casual Conversations (Book 1)
Laugh and learn with ‘Comic Collections’ by Cassia North – a delightful dive into everyday conversations in professional and casual settings, now in a vibrant, humor-filled ebook. Perfect for all ages!
Check out our Blogs!
Read our everyday blogs and gain new knowledge, skills, and inspiration to support your learning journey here in SEKAEL.


Learn through Common English Errors Blogs by recognizing and correcting everyday grammar and usage mistakes.
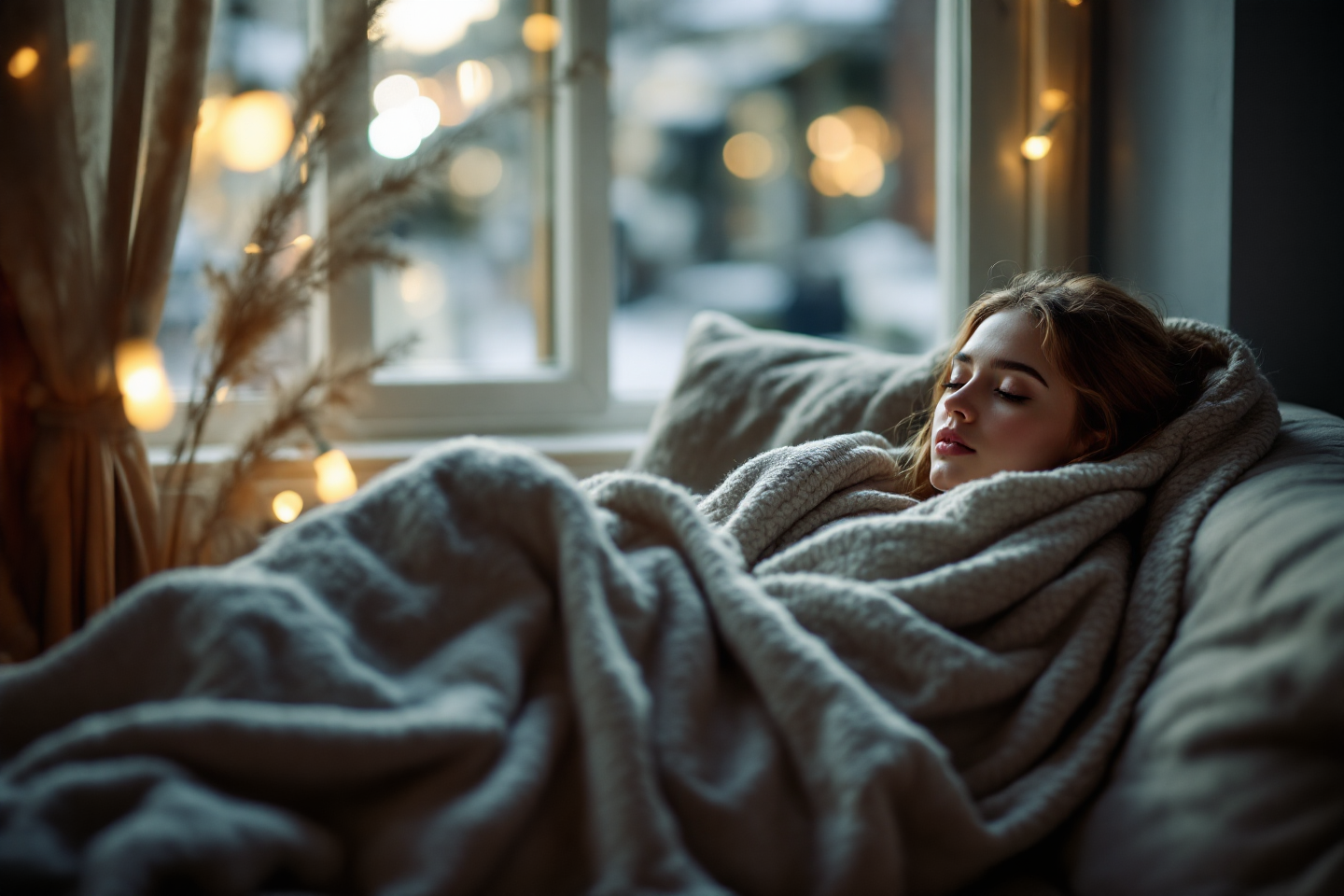








 Despite its significant impact, many people are unaware of the condition’s complexity and the seriousness with which it should be treated. SAD goes beyond feeling down during colder, darker days; it encompasses a range of symptoms that can affect every aspect of one’s life, from sleep patterns to social interactions. As we delve into the nuances of Seasonal Affective Disorder, this blog aims to shed light on its symptoms, potential causes, and the various treatment options available, offering hope and guidance for those affected by this seasonal depression. Understanding SAD is the first step toward effective management and coping strategies, ensuring those affected can navigate their symptoms with knowledge and support.
Despite its significant impact, many people are unaware of the condition’s complexity and the seriousness with which it should be treated. SAD goes beyond feeling down during colder, darker days; it encompasses a range of symptoms that can affect every aspect of one’s life, from sleep patterns to social interactions. As we delve into the nuances of Seasonal Affective Disorder, this blog aims to shed light on its symptoms, potential causes, and the various treatment options available, offering hope and guidance for those affected by this seasonal depression. Understanding SAD is the first step toward effective management and coping strategies, ensuring those affected can navigate their symptoms with knowledge and support. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a family of depression that manifests during a particular season, typically in autumn and winter, when daylight hours shorten and exposure to sunlight decreases. However, a less common form of SAD occurs during the spring and summer months, demonstrating that this condition can impact individuals differently based on the season. Unlike the mild winter blues that many people experience with the change of seasons, SAD involves significant mood changes and symptoms that can affect a person’s daily functioning.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a family of depression that manifests during a particular season, typically in autumn and winter, when daylight hours shorten and exposure to sunlight decreases. However, a less common form of SAD occurs during the spring and summer months, demonstrating that this condition can impact individuals differently based on the season. Unlike the mild winter blues that many people experience with the change of seasons, SAD involves significant mood changes and symptoms that can affect a person’s daily functioning. The prevalence of SAD varies by geography and age, with individuals living farther from the equator and younger adults being more susceptible. Women are also diagnosed with SAD at a higher rate than men. This condition highlights the complex interplay between our environment, biological rhythms, and mental health, underscoring the need for a deeper understanding and awareness of SAD.
The prevalence of SAD varies by geography and age, with individuals living farther from the equator and younger adults being more susceptible. Women are also diagnosed with SAD at a higher rate than men. This condition highlights the complex interplay between our environment, biological rhythms, and mental health, underscoring the need for a deeper understanding and awareness of SAD. Distinguishing SAD from the winter blues is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Winter blues might bring on mild feelings of downness or low energy during cold weather. However, SAD is a different story altogether. It’s characterized by much more severe symptoms like deep sadness, significant changes in sleep and appetite, and a loss of interest in things you used to enjoy. These symptoms can be incredibly disruptive, making it difficult to function normally in your daily work, school, or relationships. This highlights the importance of recognizing SAD and taking steps to address it with the seriousness it deserves. As we continue to explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for SAD, it becomes evident that this condition is more than just a seasonal funk—it’s a significant mental health issue that requires attention and care.
Distinguishing SAD from the winter blues is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Winter blues might bring on mild feelings of downness or low energy during cold weather. However, SAD is a different story altogether. It’s characterized by much more severe symptoms like deep sadness, significant changes in sleep and appetite, and a loss of interest in things you used to enjoy. These symptoms can be incredibly disruptive, making it difficult to function normally in your daily work, school, or relationships. This highlights the importance of recognizing SAD and taking steps to address it with the seriousness it deserves. As we continue to explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for SAD, it becomes evident that this condition is more than just a seasonal funk—it’s a significant mental health issue that requires attention and care. Seasonal Affective Disorder manifests through a variety of symptoms, which can vary significantly depending on whether the individual is experiencing winter-pattern or summer-pattern SAD. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for recognizing the condition and seeking appropriate treatment.
Seasonal Affective Disorder manifests through a variety of symptoms, which can vary significantly depending on whether the individual is experiencing winter-pattern or summer-pattern SAD. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for recognizing the condition and seeking appropriate treatment. Unfortunately, these symptoms aren’t just inconvenient. They can have a major impact on your quality of life. This can influence your relationships with friends and family, make it hard to focus at work or school, and leave you feeling drained overall. It’s important to note that while some symptoms are common to other forms of depression, the seasonal recurrence of these symptoms is a key indicator of SAD. This cyclical pattern not only aids in diagnosing the disorder but also emphasizes the profound effect seasonal changes can have on our mental health. Recognizing these symptoms as part of a recurring pattern is the first step toward seeking help and finding effective treatment options to manage SAD.
Unfortunately, these symptoms aren’t just inconvenient. They can have a major impact on your quality of life. This can influence your relationships with friends and family, make it hard to focus at work or school, and leave you feeling drained overall. It’s important to note that while some symptoms are common to other forms of depression, the seasonal recurrence of these symptoms is a key indicator of SAD. This cyclical pattern not only aids in diagnosing the disorder but also emphasizes the profound effect seasonal changes can have on our mental health. Recognizing these symptoms as part of a recurring pattern is the first step toward seeking help and finding effective treatment options to manage SAD.





 Diagnosing Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) involves a comprehensive assessment by a mental health professional. Given its symptomatic overlap with other forms of depression, distinguishing SAD from general depression or other mental health conditions is crucial. The diagnostic process typically includes a thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, a physical exam, and detailed discussions about the nature and timing of the symptoms.
Diagnosing Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) involves a comprehensive assessment by a mental health professional. Given its symptomatic overlap with other forms of depression, distinguishing SAD from general depression or other mental health conditions is crucial. The diagnostic process typically includes a thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, a physical exam, and detailed discussions about the nature and timing of the symptoms. The cyclical nature of SAD can complicate its diagnosis. Patients might not immediately recognize the seasonal pattern of their symptoms or may not seek help during active episodes. Furthermore, other conditions like thyroid disorders can mimic the symptoms of depression, necessitating a careful exclusion of medical causes.
The cyclical nature of SAD can complicate its diagnosis. Patients might not immediately recognize the seasonal pattern of their symptoms or may not seek help during active episodes. Furthermore, other conditions like thyroid disorders can mimic the symptoms of depression, necessitating a careful exclusion of medical causes. While self-assessment tools and questionnaires can be helpful in identifying potential cases of SAD, they cannot replace professional diagnosis. These tools can, however, provide valuable insights that individuals can bring to their healthcare provider to facilitate the diagnostic process.
While self-assessment tools and questionnaires can be helpful in identifying potential cases of SAD, they cannot replace professional diagnosis. These tools can, however, provide valuable insights that individuals can bring to their healthcare provider to facilitate the diagnostic process.




 Create a Support System:
Create a Support System: Establish a Routine:
Establish a Routine: Stay Active: Don’t underestimate the power of exercise! It’s a fantastic tool to combat SAD. Even low-impact activities like yoga or walking can be incredibly beneficial. They act like natural mood boosters, increasing your energy and overall well-being. So next time you’re feeling the winter blues, lace up your shoes or grab your yoga mat – it might be just the pick-me-up you need. Whenever possible, outdoor exercise during daylight hours can double the benefits of combining physical activity with sunlight exposure.
Stay Active: Don’t underestimate the power of exercise! It’s a fantastic tool to combat SAD. Even low-impact activities like yoga or walking can be incredibly beneficial. They act like natural mood boosters, increasing your energy and overall well-being. So next time you’re feeling the winter blues, lace up your shoes or grab your yoga mat – it might be just the pick-me-up you need. Whenever possible, outdoor exercise during daylight hours can double the benefits of combining physical activity with sunlight exposure. Seek Professional Help Early:
Seek Professional Help Early: Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is essential for those affected and their loved ones. By recognizing its symptoms and underlying causes and exploring available treatments, individuals can navigate this condition more effectively. Treatments like light therapy, medication, and cognitive behavioral therapy, along with lifestyle adjustments, offer a beacon of hope for managing SAD. If you’re struggling with seasonal depression, there’s hope! By building a strong support system with friends, family, or even a support group, you can create a positive environment that makes a big difference. Don’t wait to reach out for help! Talking to a professional can be very transformational. They can equip you with everything you might need to effectively manage your SAD symptoms. This will empower you to take control and feel better, even during challenging seasons. Remember, taking these steps can significantly improve your quality of life, even during those tough seasonal dips. Awareness and proactive management are key, enabling individuals to not just endure the changing seasons but thrive throughout the year.
Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is essential for those affected and their loved ones. By recognizing its symptoms and underlying causes and exploring available treatments, individuals can navigate this condition more effectively. Treatments like light therapy, medication, and cognitive behavioral therapy, along with lifestyle adjustments, offer a beacon of hope for managing SAD. If you’re struggling with seasonal depression, there’s hope! By building a strong support system with friends, family, or even a support group, you can create a positive environment that makes a big difference. Don’t wait to reach out for help! Talking to a professional can be very transformational. They can equip you with everything you might need to effectively manage your SAD symptoms. This will empower you to take control and feel better, even during challenging seasons. Remember, taking these steps can significantly improve your quality of life, even during those tough seasonal dips. Awareness and proactive management are key, enabling individuals to not just endure the changing seasons but thrive throughout the year.









 This post examines the complex correlation between mental health and social media use, providing knowledge, research discoveries, and useful tips for managing the online world without impacting mental wellness. By unraveling the various aspects of this subject, we strive to uncover the ways in which social media impacts our mental state and how we can develop a better relationship with these channels, promoting better overall mental health. Understanding this link is crucial, not only for individual users but for society as a whole, as we move forward in an increasingly connected world.
This post examines the complex correlation between mental health and social media use, providing knowledge, research discoveries, and useful tips for managing the online world without impacting mental wellness. By unraveling the various aspects of this subject, we strive to uncover the ways in which social media impacts our mental state and how we can develop a better relationship with these channels, promoting better overall mental health. Understanding this link is crucial, not only for individual users but for society as a whole, as we move forward in an increasingly connected world. The journey of social media from its nascent stages to becoming a global phenomenon is nothing short of remarkable. The evolution began in the late 1990s and early 2000s with sites like Six Degrees and Friendster, which laid the groundwork for the social networking revolution. These platforms introduced the concept of creating personal profiles and connecting with friends online, setting the stage for future innovations in digital socialization. The subsequent launch of Facebook in 2004 marked a pivotal moment, transforming social media into a ubiquitous presence in our lives. Today, with the advent of platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok, social media has diversified, catering to varied interests and forms of expression.
The journey of social media from its nascent stages to becoming a global phenomenon is nothing short of remarkable. The evolution began in the late 1990s and early 2000s with sites like Six Degrees and Friendster, which laid the groundwork for the social networking revolution. These platforms introduced the concept of creating personal profiles and connecting with friends online, setting the stage for future innovations in digital socialization. The subsequent launch of Facebook in 2004 marked a pivotal moment, transforming social media into a ubiquitous presence in our lives. Today, with the advent of platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok, social media has diversified, catering to varied interests and forms of expression. Current statistics highlight the staggering extent of social media’s reach, with over 4.5 billion people around the world actively using these platforms. This represents more than half of the global population, a testament to social media’s integral role in modern communication. These platforms have not only reshaped how we connect with others but have also become vital tools for business, activism, and entertainment. They offer unprecedented opportunities for individuals to share their lives, opinions, and talents with a global audience, fostering communities and movements that transcend geographical boundaries.
Current statistics highlight the staggering extent of social media’s reach, with over 4.5 billion people around the world actively using these platforms. This represents more than half of the global population, a testament to social media’s integral role in modern communication. These platforms have not only reshaped how we connect with others but have also become vital tools for business, activism, and entertainment. They offer unprecedented opportunities for individuals to share their lives, opinions, and talents with a global audience, fostering communities and movements that transcend geographical boundaries. The way we communicate and our perception of ourselves and the world around us have been greatly impacted by the escalation of social media. Society has been transformed by this phenomenon. Its impact is multifaceted, serving as a tool for empowerment and connection while also posing challenges and questions about privacy, authenticity, and mental well-being. As we delve deeper into the relationship between social media and mental health, it’s essential to consider this historical context and the profound influence these platforms wield in our daily lives.
The way we communicate and our perception of ourselves and the world around us have been greatly impacted by the escalation of social media. Society has been transformed by this phenomenon. Its impact is multifaceted, serving as a tool for empowerment and connection while also posing challenges and questions about privacy, authenticity, and mental well-being. As we delve deeper into the relationship between social media and mental health, it’s essential to consider this historical context and the profound influence these platforms wield in our daily lives.
 An individual’s mood, thought processes, and daily functioning can be influenced by common mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Each of these disorders has its own set of symptoms. Anxiety and depression, for example, can lead to persistent feelings of worry or sadness, affecting an individual’s ability to work, study, eat, sleep, and enjoy life. Despite the prevalence of these conditions—millions worldwide suffer from mental health issues—they often go unrecognized or untreated due to lack of awareness, access to care, or the stigma attached to admitting one struggles with mental health.
An individual’s mood, thought processes, and daily functioning can be influenced by common mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Each of these disorders has its own set of symptoms. Anxiety and depression, for example, can lead to persistent feelings of worry or sadness, affecting an individual’s ability to work, study, eat, sleep, and enjoy life. Despite the prevalence of these conditions—millions worldwide suffer from mental health issues—they often go unrecognized or untreated due to lack of awareness, access to care, or the stigma attached to admitting one struggles with mental health. In recent years, there has been a growing movement to destigmatize mental health issues, with public figures, organizations, and individuals advocating for open discussions, increased funding for mental health services, and greater access to care. Social media, while a double-edged sword, has played a significant role in this shift, offering platforms where people can share their experiences, find community, and access information and support. Understanding the fundamental aspects of mental health is the first step in exploring its complex relationship with social media, highlighting the need for a balanced approach to digital consumption for the sake of our psychological well-being.
In recent years, there has been a growing movement to destigmatize mental health issues, with public figures, organizations, and individuals advocating for open discussions, increased funding for mental health services, and greater access to care. Social media, while a double-edged sword, has played a significant role in this shift, offering platforms where people can share their experiences, find community, and access information and support. Understanding the fundamental aspects of mental health is the first step in exploring its complex relationship with social media, highlighting the need for a balanced approach to digital consumption for the sake of our psychological well-being. The relationship between mental health and social media is a complex issue, where studies shed light on the diverse effects these networks have on our psychological state, highlighting both beneficial and detrimental outcomes. On the positive side, social media offers unparalleled opportunities for connectivity, allowing individuals to maintain relationships across distances, find communities of support, and access a wealth of informational resources. For many, these platforms are a space for self-expression and identity exploration, offering a sense of belonging and validation. Awareness campaigns and support communities on social media platforms have been pivotal in reducing the stigma around mental health, offering people the knowledge and motivation necessary to pursue assistance.
The relationship between mental health and social media is a complex issue, where studies shed light on the diverse effects these networks have on our psychological state, highlighting both beneficial and detrimental outcomes. On the positive side, social media offers unparalleled opportunities for connectivity, allowing individuals to maintain relationships across distances, find communities of support, and access a wealth of informational resources. For many, these platforms are a space for self-expression and identity exploration, offering a sense of belonging and validation. Awareness campaigns and support communities on social media platforms have been pivotal in reducing the stigma around mental health, offering people the knowledge and motivation necessary to pursue assistance. Yet, the link between social media and mental health isn’t entirely positive. An increasing amount of studies highlight the negative consequences of too much social media use, such as heightened levels of stress, depression, and isolation. A major issue is the culture of comparison driven by sites like Instagram and Facebook, where viewing others’ curated life highlights can provoke feelings of insufficiency and low self-worth in viewers. The obligation to maintain an impeccable online persona can also lead to anxiety and stress, especially in teenagers and young adults who are more vulnerable to social approval.
Yet, the link between social media and mental health isn’t entirely positive. An increasing amount of studies highlight the negative consequences of too much social media use, such as heightened levels of stress, depression, and isolation. A major issue is the culture of comparison driven by sites like Instagram and Facebook, where viewing others’ curated life highlights can provoke feelings of insufficiency and low self-worth in viewers. The obligation to maintain an impeccable online persona can also lead to anxiety and stress, especially in teenagers and young adults who are more vulnerable to social approval. Another point of concern is how social media affects sleep. Screen-emitted blue light can interfere with regular sleep patterns, and the compelling draw of these platforms frequently leads to prolonged use before bedtime, exacerbating sleep quality issues. Inadequate sleep quality is acknowledged as a factor in numerous mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
Another point of concern is how social media affects sleep. Screen-emitted blue light can interfere with regular sleep patterns, and the compelling draw of these platforms frequently leads to prolonged use before bedtime, exacerbating sleep quality issues. Inadequate sleep quality is acknowledged as a factor in numerous mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. The algorithms powering social media platforms are designed to capture and retain user attention, often with profound effects on our emotions and behaviors. These algorithms analyze user interactions, preferences, and activity patterns to curate and present content they predict will be most engaging. While this can enhance user experience by tailoring content to individual interests, it also raises concerns about the psychological impact of such personalized feeds.
The algorithms powering social media platforms are designed to capture and retain user attention, often with profound effects on our emotions and behaviors. These algorithms analyze user interactions, preferences, and activity patterns to curate and present content they predict will be most engaging. While this can enhance user experience by tailoring content to individual interests, it also raises concerns about the psychological impact of such personalized feeds. The addictive nature of social media is another consequence of algorithmic design. Features like infinite scrolling and notification badges exploit human psychological vulnerabilities, encouraging continuous platform use. This can lead to excessive screen time, disrupting real-life interactions, physical activity, and sleep—all critical components of mental health. The dopamine-driven feedback loops associated with likes, comments, and shares can also mimic the effects of addictive substances, making it difficult for users to disengage.
The addictive nature of social media is another consequence of algorithmic design. Features like infinite scrolling and notification badges exploit human psychological vulnerabilities, encouraging continuous platform use. This can lead to excessive screen time, disrupting real-life interactions, physical activity, and sleep—all critical components of mental health. The dopamine-driven feedback loops associated with likes, comments, and shares can also mimic the effects of addictive substances, making it difficult for users to disengage. Furthermore, algorithms can inadvertently promote harmful content, including disinformation, extreme dieting practices, or self-harm, which can have dire consequences for vulnerable users. Although platforms are increasingly implementing measures to mitigate these risks, the challenge of balancing user engagement with mental health considerations remains significant.
Furthermore, algorithms can inadvertently promote harmful content, including disinformation, extreme dieting practices, or self-harm, which can have dire consequences for vulnerable users. Although platforms are increasingly implementing measures to mitigate these risks, the challenge of balancing user engagement with mental health considerations remains significant. As we navigate the complexities of the digital age, the link between social media and mental health emerges as a critical area of concern and study. Our exploration reveals a nuanced landscape where the benefits of connectivity and community coexist with challenges such as anxiety, depression, and disrupted self-esteem. Acknowledging the two-sided character of social media is the initial move in cultivating a more positive engagement with these networks.
As we navigate the complexities of the digital age, the link between social media and mental health emerges as a critical area of concern and study. Our exploration reveals a nuanced landscape where the benefits of connectivity and community coexist with challenges such as anxiety, depression, and disrupted self-esteem. Acknowledging the two-sided character of social media is the initial move in cultivating a more positive engagement with these networks. In closing, the conversation about social media and mental health is ongoing, reflecting broader societal shifts toward recognizing and valuing mental wellness. By approaching social media with intentionality and mindfulness, we can harness its potential for good, making our digital lives a source of support, inspiration, and connection. As we move forward, let us remain committed to balancing our online and offline lives, ensuring that our engagement with social media enriches rather than detracts from our overall well-being.
In closing, the conversation about social media and mental health is ongoing, reflecting broader societal shifts toward recognizing and valuing mental wellness. By approaching social media with intentionality and mindfulness, we can harness its potential for good, making our digital lives a source of support, inspiration, and connection. As we move forward, let us remain committed to balancing our online and offline lives, ensuring that our engagement with social media enriches rather than detracts from our overall well-being.








 Personal stories and case studies further illustrate mindfulness’s impact on mental health. Many people have reported that practicing mindfulness has helped them to make significant progress in reducing their symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression while also increasing their overall happiness and satisfaction with life. The following accounts exhibit how practicing mindfulness can help individuals enhance their mental well-being.
Personal stories and case studies further illustrate mindfulness’s impact on mental health. Many people have reported that practicing mindfulness has helped them to make significant progress in reducing their symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression while also increasing their overall happiness and satisfaction with life. The following accounts exhibit how practicing mindfulness can help individuals enhance their mental well-being.






 The integration of mindfulness into psychological therapy has revolutionized traditional approaches to mental health treatment. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is a standout example, combining cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) principles with mindfulness strategies. Developed to prevent the recurrence of depression, MBCT teaches individuals to disengage from automatic negative thought patterns that can trigger depressive episodes.
The integration of mindfulness into psychological therapy has revolutionized traditional approaches to mental health treatment. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is a standout example, combining cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) principles with mindfulness strategies. Developed to prevent the recurrence of depression, MBCT teaches individuals to disengage from automatic negative thought patterns that can trigger depressive episodes. Their sessions, finding that these practices help clients develop a more compassionate and non-judgmental awareness of their thoughts and feelings. Changing one’s perspective is an effective way for people to better manage their emotional reactions and minimize the impact of stressful thoughts and feelings on their mental well-being, which is crucial when it comes to handling stress. This shift in outlook is essential in coping with stress and can result in a more optimistic approach to life. By altering the way they view challenging situations, people can maintain better control over their emotions and avoid harmful thought patterns that can contribute to mental health issues. This shift in mindset is an effective way to manage stress and improve overall well-being.
Their sessions, finding that these practices help clients develop a more compassionate and non-judgmental awareness of their thoughts and feelings. Changing one’s perspective is an effective way for people to better manage their emotional reactions and minimize the impact of stressful thoughts and feelings on their mental well-being, which is crucial when it comes to handling stress. This shift in outlook is essential in coping with stress and can result in a more optimistic approach to life. By altering the way they view challenging situations, people can maintain better control over their emotions and avoid harmful thought patterns that can contribute to mental health issues. This shift in mindset is an effective way to manage stress and improve overall well-being. The effectiveness of mindfulness in therapy is supported by a growing body of research. Studies have shown that incorporating mindfulness techniques can result in a notable reduction in symptoms related to anxiety, depression, and PTSD. This makes mindfulness a valuable addition to more conventional therapeutic methods. Furthermore, mindfulness encourages a proactive approach to mental health, empowering individuals with tools they can use outside of therapy to maintain and improve their mental well-being.
The effectiveness of mindfulness in therapy is supported by a growing body of research. Studies have shown that incorporating mindfulness techniques can result in a notable reduction in symptoms related to anxiety, depression, and PTSD. This makes mindfulness a valuable addition to more conventional therapeutic methods. Furthermore, mindfulness encourages a proactive approach to mental health, empowering individuals with tools they can use outside of therapy to maintain and improve their mental well-being. By fostering an attitude of acceptance and present-moment awareness, mindfulness in therapy helps individuals confront their challenges with resilience and clarity. This approach not only aids in the healing process but also contributes to a more fulfilling and balanced life.
By fostering an attitude of acceptance and present-moment awareness, mindfulness in therapy helps individuals confront their challenges with resilience and clarity. This approach not only aids in the healing process but also contributes to a more fulfilling and balanced life.














 Mindfulness offers a profound tool for navigating the complexities of modern life with grace and resilience. By anchoring us in the present moment, mindfulness cuts through the noise of daily distractions and unveils a space of clarity and calm within ourselves. This journey, though personal and unique for each individual, holds universal truths about the power of awareness, acceptance, and the capacity for transformation.
Mindfulness offers a profound tool for navigating the complexities of modern life with grace and resilience. By anchoring us in the present moment, mindfulness cuts through the noise of daily distractions and unveils a space of clarity and calm within ourselves. This journey, though personal and unique for each individual, holds universal truths about the power of awareness, acceptance, and the capacity for transformation. Now that we see How Mindfulness Can Transform Your Mental Health by looking at the benefits of mindfulness extend far beyond the moments of meditation; they weave through every aspect of our lives, enhancing our relationships, productivity, and overall satisfaction. As we move forward, the invitation is to continue exploring mindfulness with curiosity and openness, integrating its practices into our daily routines and moments of need.
Now that we see How Mindfulness Can Transform Your Mental Health by looking at the benefits of mindfulness extend far beyond the moments of meditation; they weave through every aspect of our lives, enhancing our relationships, productivity, and overall satisfaction. As we move forward, the invitation is to continue exploring mindfulness with curiosity and openness, integrating its practices into our daily routines and moments of need. The path of mindfulness is one of continuous discovery and growth. There may be challenges and setbacks, but each step taken is a step toward greater mental health and a fuller, more engaged life. Let mindfulness be your guide, a constant cowell-being in the pursuit of well-being and inner peace.
The path of mindfulness is one of continuous discovery and growth. There may be challenges and setbacks, but each step taken is a step toward greater mental health and a fuller, more engaged life. Let mindfulness be your guide, a constant cowell-being in the pursuit of well-being and inner peace.




 In today’s relentlessly fast-paced world, the line between pushing oneself for success and falling into burnout has become dangerously thin. Burnout, characterized by emotional, physical, and mental fatigue resulting from intense and extended stress, has become a silent epidemic among individuals and workers trying to keep up with the increasing pressures of work and personal life. It’s a condition that sneaks up quietly, often mistaken for mere tiredness or a temporary bout of stress. Yet, its impact can be profound and long-lasting, affecting health, happiness, and job performance.
In today’s relentlessly fast-paced world, the line between pushing oneself for success and falling into burnout has become dangerously thin. Burnout, characterized by emotional, physical, and mental fatigue resulting from intense and extended stress, has become a silent epidemic among individuals and workers trying to keep up with the increasing pressures of work and personal life. It’s a condition that sneaks up quietly, often mistaken for mere tiredness or a temporary bout of stress. Yet, its impact can be profound and long-lasting, affecting health, happiness, and job performance. Understanding and recognizing the signs of burnout is the first critical step toward recovery. However, identifying burnout can be tricky, especially when its symptoms overlap with everyday stress. This makes it all the more essential to distinguish between being just stressed and being burnt out. Stress involves excessive demands: too many pressures that exhaust you physically and mentally. Yet, those under stress often believe that managing everything will improve their situation. In contrast, burnout relates to a deficiency: feeling empty, lacking motivation, and no longer caring. Those suffering from burnout typically see no hopeful prospects for improvement in their circumstances.
Understanding and recognizing the signs of burnout is the first critical step toward recovery. However, identifying burnout can be tricky, especially when its symptoms overlap with everyday stress. This makes it all the more essential to distinguish between being just stressed and being burnt out. Stress involves excessive demands: too many pressures that exhaust you physically and mentally. Yet, those under stress often believe that managing everything will improve their situation. In contrast, burnout relates to a deficiency: feeling empty, lacking motivation, and no longer caring. Those suffering from burnout typically see no hopeful prospects for improvement in their circumstances. You might be on the burnout spectrum if you’re feeling constantly drained, detached, and disillusioned. The good news is that burnout is manageable and reversible. By using both self-help techniques and professional assistance, you can restore your balance and find renewed pleasure in your work and life. This guide delves into the ten signs that signify you might be experiencing burnout and offers practical, actionable strategies to embark on recovery. By acknowledging the problem and taking decisive steps to address it, you can rebuild your reserves of energy and enthusiasm and find a more sustainable way of living and working.
You might be on the burnout spectrum if you’re feeling constantly drained, detached, and disillusioned. The good news is that burnout is manageable and reversible. By using both self-help techniques and professional assistance, you can restore your balance and find renewed pleasure in your work and life. This guide delves into the ten signs that signify you might be experiencing burnout and offers practical, actionable strategies to embark on recovery. By acknowledging the problem and taking decisive steps to address it, you can rebuild your reserves of energy and enthusiasm and find a more sustainable way of living and working.



















 As we navigate the complexities of modern life, the shadow of burnout looms large, threatening to undermine our health, happiness, and professional success. Recognizing the signs of burnout is the first critical step toward reclaiming your well-being and vitality. The journey from burnout to recovery is personal and can require a multifaceted approach, incorporating changes to your work habits, lifestyle, and mindset.
As we navigate the complexities of modern life, the shadow of burnout looms large, threatening to undermine our health, happiness, and professional success. Recognizing the signs of burnout is the first critical step toward reclaiming your well-being and vitality. The journey from burnout to recovery is personal and can require a multifaceted approach, incorporating changes to your work habits, lifestyle, and mindset. Beyond individual efforts, there’s a growing recognition of the need for systemic changes to address the root causes of burnout. Employers play a crucial role in creating work environments that promote work-life balance, support mental health, and recognize the importance of rest and recovery. Creating a work environment that emphasizes both physical and mental health can stop burnout before it starts and keep everyone feeling their best.
Beyond individual efforts, there’s a growing recognition of the need for systemic changes to address the root causes of burnout. Employers play a crucial role in creating work environments that promote work-life balance, support mental health, and recognize the importance of rest and recovery. Creating a work environment that emphasizes both physical and mental health can stop burnout before it starts and keep everyone feeling their best. Burnout is a signal that something in your life is out of alignment. It’s an invitation to pause, reflect, and make meaningful changes that support your health and happiness. By acknowledging the signs of burnout and taking proactive steps toward recovery, you can navigate back to a life of balance, fulfillment, and joy. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. With the right support and strategies, recovery is possible and can be a transformative experience that leads to a more satisfying and sustainable way of living.
Burnout is a signal that something in your life is out of alignment. It’s an invitation to pause, reflect, and make meaningful changes that support your health and happiness. By acknowledging the signs of burnout and taking proactive steps toward recovery, you can navigate back to a life of balance, fulfillment, and joy. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. With the right support and strategies, recovery is possible and can be a transformative experience that leads to a more satisfying and sustainable way of living.




 This guide aims to shed light on the multifaceted nature of anxiety, providing a comprehensive exploration of strategies and tools to manage it effectively. It delves into both psychological and practical approaches, offering a balanced perspective on anxiety management.
This guide aims to shed light on the multifaceted nature of anxiety, providing a comprehensive exploration of strategies and tools to manage it effectively. It delves into both psychological and practical approaches, offering a balanced perspective on anxiety management.










 The right strategies and tools can make a significant difference in this journey. Psychological approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy can aid in understanding and altering thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. Physical strategies, including regular exercise and a healthy diet, can reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety. Lifestyle strategies, such as mindfulness and meditation, can help you stay present and focused, reducing anxiety’s impact on your day-to-day life.
The right strategies and tools can make a significant difference in this journey. Psychological approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy can aid in understanding and altering thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. Physical strategies, including regular exercise and a healthy diet, can reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety. Lifestyle strategies, such as mindfulness and meditation, can help you stay present and focused, reducing anxiety’s impact on your day-to-day life. Keep in mind that seeking professional assistance when necessary is not an indication of weakness, but a demonstration of strength. It requires bravery to ask for help. Therapists and counselors are trained experts who can offer you more strategies and tools to cope with your anxiety.
Keep in mind that seeking professional assistance when necessary is not an indication of weakness, but a demonstration of strength. It requires bravery to ask for help. Therapists and counselors are trained experts who can offer you more strategies and tools to cope with your anxiety.